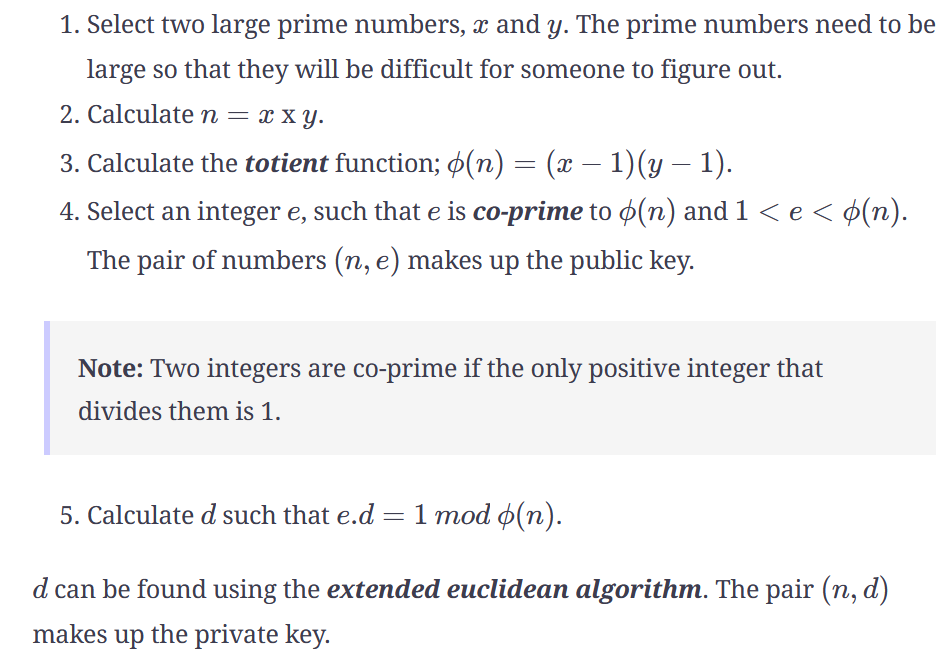
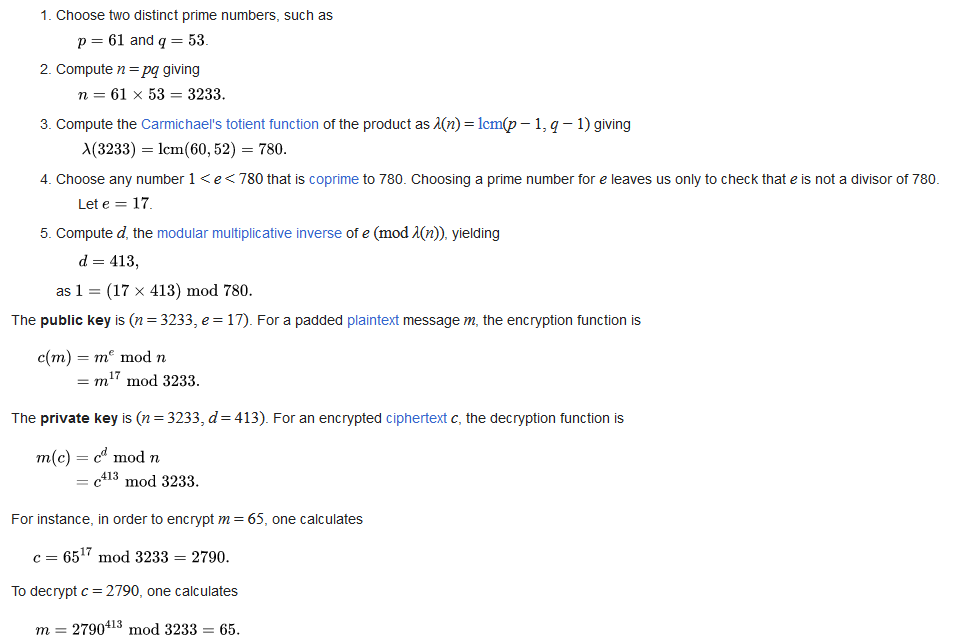
This week we are going to look at security issues within an operating system. We will look at the RSA encryption alorithm.
We will also look at authentication and encryption with openssl.
| Name of the Algorithm | Short Description of the Algorithm | Efficacy |
|---|
| RSA (Rivest-Shamir-Adleman) |
One of the most widely used public-key cryptosystems, based on the difficulty of factoring large integers. Commonly used for secure communications and digital signatures. | Strong at key sizes ≥2048 bits; susceptible to quantum attacks. |
| ECC (Elliptic Curve Cryptography) |
Uses elliptic curves over finite fields for encryption, offering the same security as RSA with much smaller key sizes. Common in modern secure communications. | More efficient than RSA at smaller key sizes; resistant to many classical attacks. |
| ElGamal |
Based on the discrete logarithm problem, commonly used for encryption and digital signatures. Forms the basis for DSA (Digital Signature Algorithm). | Secure with large key sizes; inefficient due to message expansion. |
| Diffie-Hellman (DH) |
Used for secure key exchange rather than encryption itself, based on the difficulty of computing discrete logarithms. | Strong with long key sizes; vulnerable to MITM attacks without authentication. |
| DSA (Digital Signature Algorithm) |
Used for digital signatures, derived from ElGamal, providing authentication and integrity verification. | Strong but requires a good random number generator; less efficient than ECC. |
| Paillier |
A homomorphic encryption scheme that allows computations on encrypted data without decryption. | Secure but computationally expensive, mainly used in privacy-preserving applications. |
| McEliece |
A lesser-known algorithm based on error-correcting codes, resistant to quantum attacks. | Very strong against classical and quantum attacks, but requires large key sizes. |